Linked List and Types of Link
A linked list is a sequence of data elements, which are connected together via links. Each data element contains a connection to another data element in form of a pointer. Python does not have linked lists in its standard library. We implement the concept of linked lists using the concept of nodes as discussed in the previous chapter. We have already seen how we create a node class and how to traverse the elements of a node. In this chapter we are going to study the types of linked lists known as singly linked lists. In this type of data structure there is only one link between any two data elements. We create such a list and create additional methods to insert, update and remove elements from the list.
ListTypes of Linked List - Singly linked, doubly linked and circular.
In this tutorial, you will learn different types of linked list. Also, you will find implementation of linked list in C.
Before you learn about the type of the linked list, make sure you know about the Linked List Data Structure.
There are three common types of Linked List.
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
Singly Linked List
It is the most common. Each node has data and a pointer to the next node.
Node is represented as:
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
}A three-member singly linked list can be created as:
/* Initialize nodes */
struct node *head;
struct node *one = NULL;
struct node *two = NULL;
struct node *three = NULL;
/* Allocate memory */
one = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
two = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
three = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* Assign data values */
one->data = 1;
two->data = 2;
three->data = 3;
/* Connect nodes */
one->next = two;
two->next = three;
three->next = NULL;
/* Save address of first node in head */
head = one;Doubly Linked List
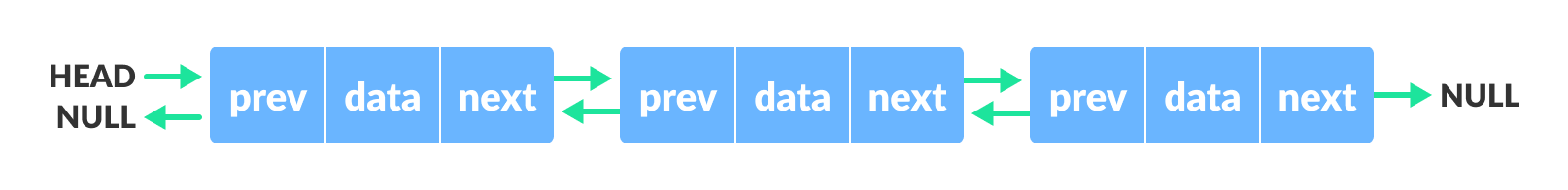
We add a pointer to the previous node in a doubly-linked list. Thus, we can go in either direction: forward or backward.
A node is represented as
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
}A three-member doubly linked list can be created as
/* Initialize nodes */
struct node *head;
struct node *one = NULL;
struct node *two = NULL;
struct node *three = NULL;
/* Allocate memory */
one = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
two = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
three = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* Assign data values */
one->data = 1;
two->data = 2;
three->data = 3;
/* Connect nodes */
one->next = two;
one->prev = NULL;
two->next = three;
two->prev = one;
three->next = NULL;
three->prev = two;
/* Save address of first node in head */
head = one;Circular Linked List
A circular linked list is a variation of a linked list in which the last element is linked to the first element. This forms a circular loop.
A circular linked list can be either singly linked or doubly linked.
- for singly linked list, next pointer of last item points to the first item
- In the doubly linked list, prev pointer of the first item points to the last item as well.
A three-member circular singly linked list can be created as:
/* Initialize nodes */
struct node *head;
struct node *one = NULL;
struct node *two = NULL;
struct node *three = NULL;
/* Allocate memory */
one = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
two = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
three = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* Assign data values */
one->data = 1;
two->data = 2;
three->data = 3;
/* Connect nodes */
one->next = two;
two->next = three;
three->next = one;
/* Save address of first node in head */
head = one;

No comments:
Post a Comment